Soil Type: Sandy rich loam with good drainage and enough organic matter to keep the soil moist for healthy growth. Crop growth is optimal on soil with a pH of 6 to 7.
Land preparation: With a mould-board plough, deep turn the soil at least three to four weeks before planting. The earth should then be ploughed to a depth of 15 to 20 cm and one or two planks.
Plantation Season: Nursery: Oct-Nov Transplantation: Jan-Feb
Layout: Row-Row: 8-10inch Plant-Plant: 3-4 inch
Irrigation: 1st irrigation:7-15 days interval depending upon requirement of field
Suitable areas: Charsada, Bunir, Dir upper, Dir Lower, Chitral, Swat, Malakand, Mardan, Swabi, Mansehra, Bajour, South Waziristan, Khyber, Khurram, Muhammad Agency.
Varieties: Swat-I · Swat Selection · Desi Red · Desi White · Pulkara · NARC-2005 · Drak Red · Tirch Mir.
Fertilizer: NPK 50:35:25 kg per acre
Harvesting Time: July-Aug
Production: 7.5-10 ton per acre
Diseases
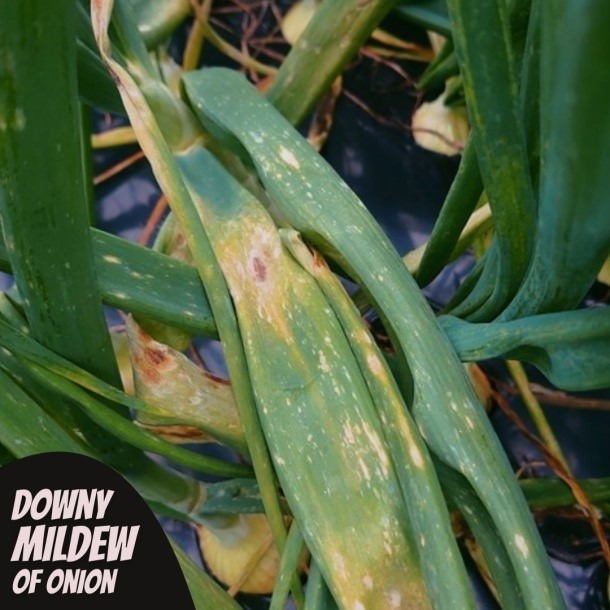
Downy Mildew
Identification: Irregular lesions are initially found on the older leaves. The leaf area under these early infections are at first a pale green colour which later become visibly more yellow. These lesions later develop a typical downy mildew grey/purple mycelium containing fruiting bodies (sporangia) which can spread spores by rain splash or over longer distances on the wind.
Management
Cultural Control
• Seeds, sets, and bulb cleaning.
• Rotation.
• The elimination of volunteers and leftover plant debris.
• Applying fungicides as soon as an infection appears.
• For this illness, decision support systems have been created.
Chemical Control
Metalaxyl, Mancozeb, Copper fungicides and chlorothalonil


Purple blotch or (Stemphylium Blight)
Identification: Brown, oval-shaped blemishes on the leaf blades. From the lesion, streaks of yellow paint the blade in both directions before turning brown. Purple blotch lesions deepen in colour as they advance and can form dark-brown concentric circles.
Management
Cultural Control
Brown, oval-shaped blemishes on the leaf blades. From the lesion, streaks of yellow paint the blade in both directions before turning brown. Purple blotch lesions deepen in colour as they advance and can form dark-brown concentric circles.
Chemical Control
Mancozeb, tebuconazole, difenaconazole and azoxystrobin
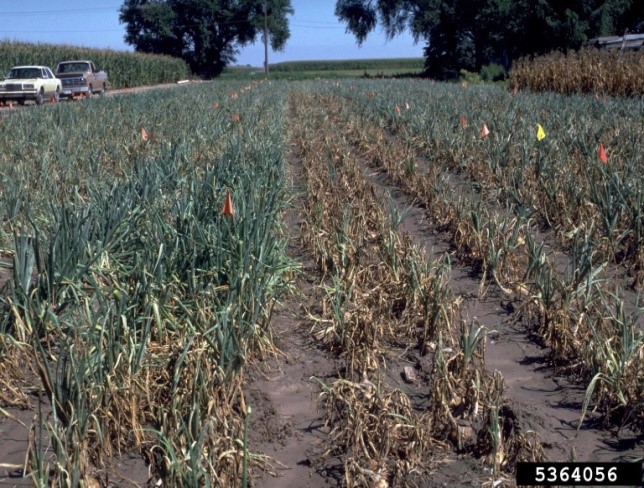


Damping off (Fusarium oxysporum)
Identification: Mold-covered, rotting seeds; pink, tan, yellow, red, or black root tips; and slowly developing seedlings that wilt and perish.
Management
Cultural Control
Sow only disease-free seed; fungicide-treat seed; alternate crops with cereals or grasses to lower pathogen levels in soil; Fusarium levels in the soil can be decreased via steam treatment or fumigation.
Chemical Control
thiophanate methyl, metalaxyl, fosetyl aluminium and Carbendazein


Insect Pest
Thrips
Identification: In plants that generate densely packed leaves, onion thrips prefer small areas and seriously harm the leaves. White spots that resemble silvery streaks on leaves are brought on by feeding. Affected tissue may become dry, yellow, and eventually brown and die as feeding continues.
Management
Cultural Control
Plant debris should be removed from gardens (and commercial fields) as well as any locations close to a spot where onions or other vulnerable vegetables will be grown.
Chemical Control
chlorfenapyr, Acetamiprid
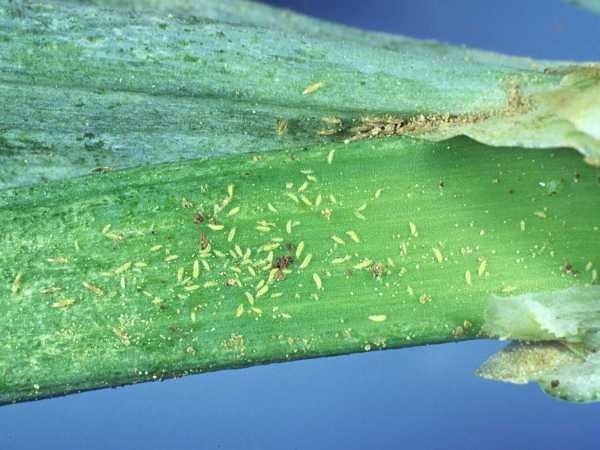


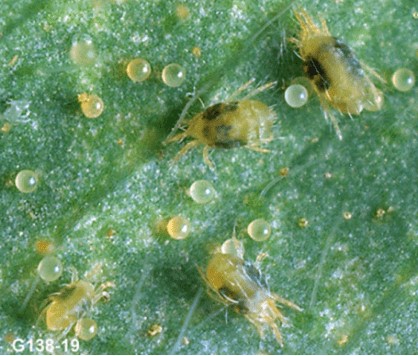
Mites
Identification: Decreased stand, stunted plant growth, decaying bulbs in the ground or storage; It is a cream-white, bulbous mite that is around 1 mm long and has legs that resemble pearls.
Management
Cultural Control
Avoid planting successive onion or onion crops in the same spot. Let the area go fallow so that any organic matter left over can completely decay. Pre-soaking onion seed cloves in hot water before planting may help minimise the number of mites present.
Chemical Control
Furadan granules