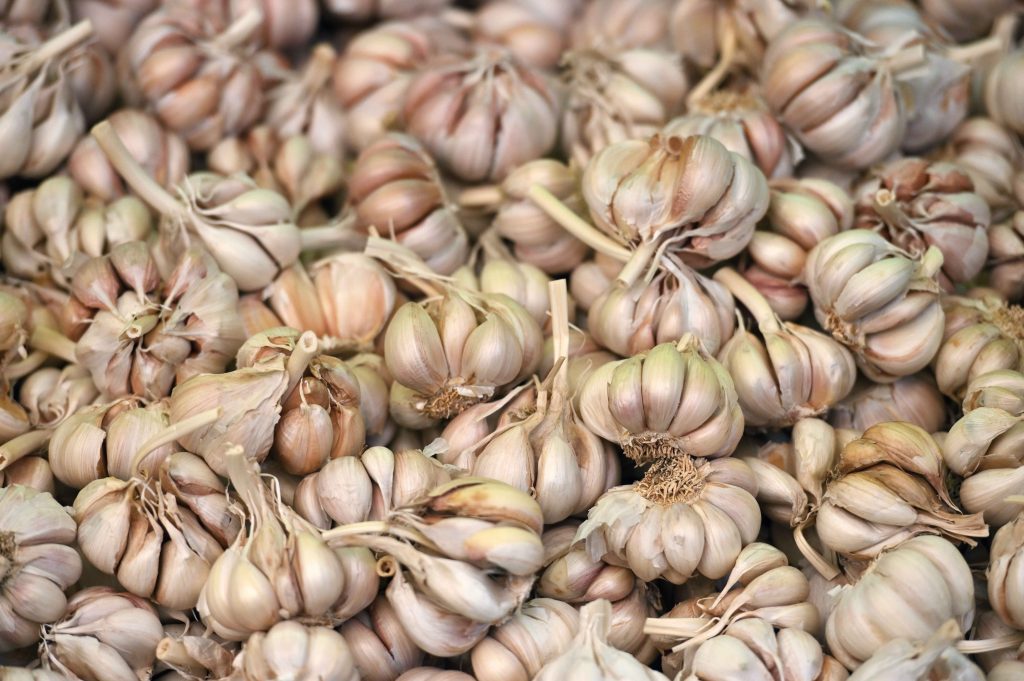

Soil Type: Fertile, well drained, loamy and airy soil is best for Garlic cultivation.
Land preparation: On intervals of 4–7 days, the field should be ploughed and harrowed twice.
Plantation Season: Aug- Oct
Layout: Plant –Plant 3-4inch, Row-Row 8-10 inch
Irrigation: Once in a week during the vegetative stage and then after 10-15 days near maturity.
Suitable areas: Bannu, Peshawar, Noshehra, Mardan, Charsada, Kohat, Swabi, Malakand, Swat
Varieties: Italian · Chinese · MJ-84 · JS-1 · NARC-G1 · Lehsan white · Pakhal Giant · NS 756 (small one), G1 Garlic.
Fertilizer: N:P:K @ 75:85:55 kg
Harvesting Time: April-May
Production: 7-10 ton per acre
Diseases
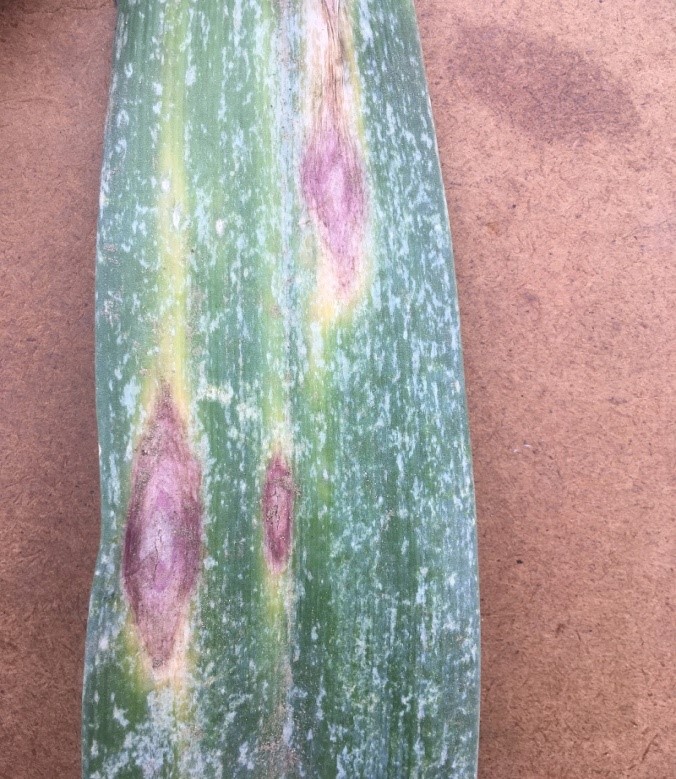
Purple Blotch garlic
Identification: The leaves of garlic have tiny white dots due to the purple blotch and later turn brown. The dots get bigger and start to become purple. The margins are reddish in colour, and a yellow circle surrounds them. The disease finally spreads across the entire leaf as the spots moved up and down the leaf.
Management
Cultural Control
Air circulation will be improved and the length of leaf wetness will be reduced with proper plant spacing and routine weeding. Don’t use too much nitrogen. For at least three years, rotate away from garlic. Field hygiene is crucial; remove or plough under plant detritus and eliminate stray plants.
Chemical Control
mancozeb, tebuconazole, difenaconazole and azoxystrobin
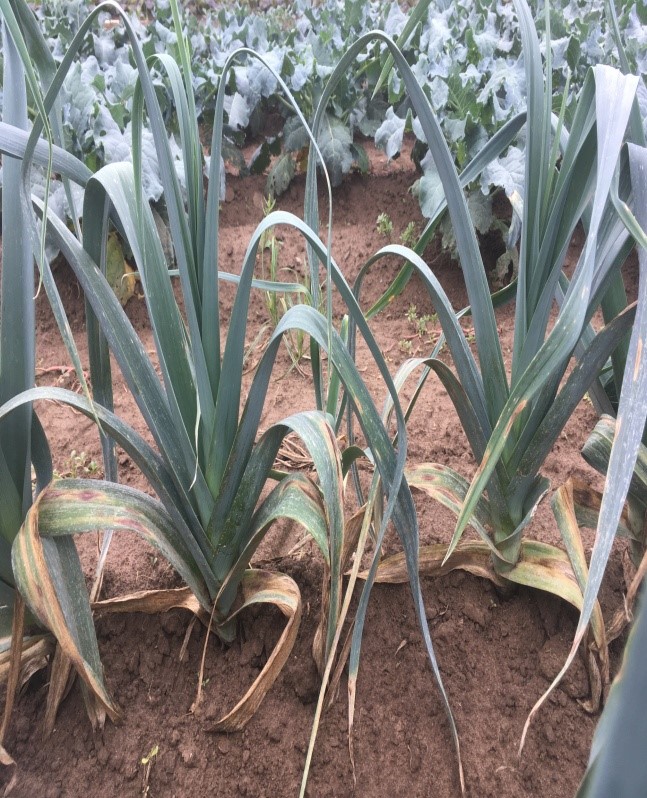


Downy Mildew:
Identification: The classic symptoms of downy mildew include a whitish, hairy growth on the leaves as well as a yellow discoloration. Both older and younger plants’ growth can be stunted by it. Leaf tips and other tissues that are distressed will eventually fall off. Bulbs kept in storage will develop a darkened neck, shrivel up, and develop wet outer scales. Some bulbs may even sprout before they should.
Management
Cultural Control
In order to decrease the prevalence of downy mildew in the field, it is crucial to have good air circulation and broad row spacing.
Chemical Control
Cymoxanil, Mancozeb
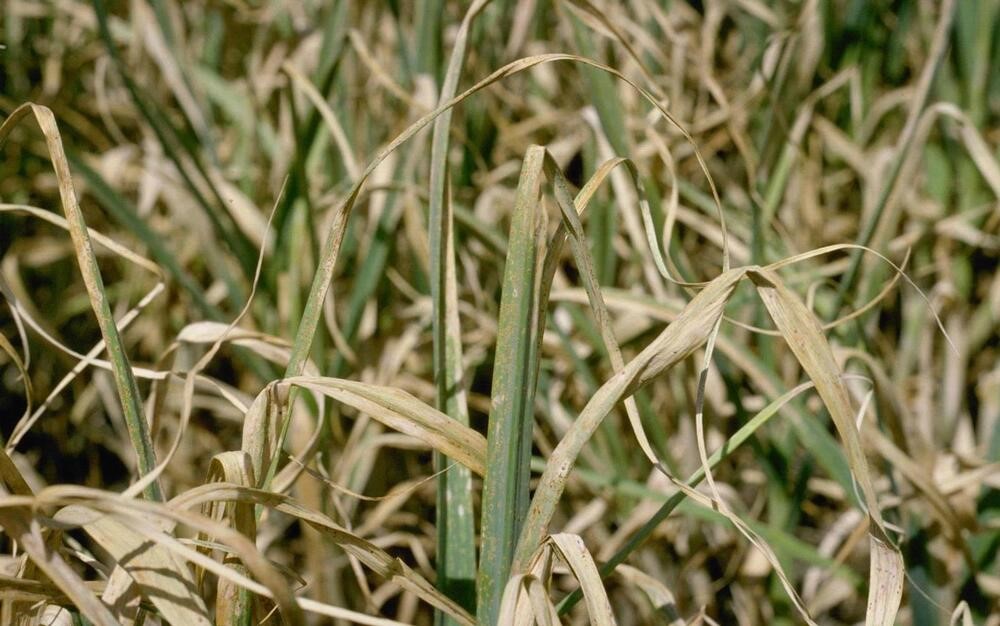


White Rot:
Identification: The stem that wraps around the base of the bulb has a white, fluffy fungal growth as one of the early indications of an infection. Sclerotia, which are tiny, black, overwintering structures, develop in the decomposing tissue.
Management
Cultural Control
- Replanting infested crops is not advised, and infested cloves should also not be planted.
- Garlic cloves can be pre-treated to help prevent white rot before planting.
- Cloves can be pre-treated with hot water by dipping them in the water just before planting, but the water shouldn’t be too hot or the cloves will die.
Chemical Control
Iprodione, tebuconazole, fludioxonil
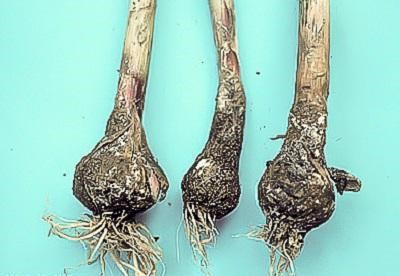

Botrytis Rot:
Identification:
Water-soaked stems and a grey, fuzzy fungal growth are two indications that a plant has Botrytis Rot. This condition is also known as “neck-rot.”
Management
Cultural Control
The best way to manage Botrytis on bulbs is to encourage rapid drying at harvest time and good aeration in storage. Moreover, colder storage temperatures might aid with disease management. Allowing adequate row spacing and adopting disease-free bulbs are essential for controlling Botrytis Rot in the pitch.
Chemical Control
Chlorothalonil, Iprodione, Mancozeb

Insect Pest
Thrips
Identification:
Adult Thirps spend the winter in debris, under bark, and other safe locations. Throughout spring, they are more active and lay their eggs that have one end that protrudes slightly, in the tissues of plants. The eggs become nymphs, which start eating flowers, buds, and leaves as soon as they hatch.
Management
Cultural Control
If at all possible, steer clear of planting onions close to grain or alfalfa fields since thrips frequently develop in those areas in the spring and move to onion fields when the grain grows or the alfalfa is cut. Rainfall and overhead irrigation both reduce thrips populations.
Chemical Control
Cypermethrin, Chlorfenapyr
